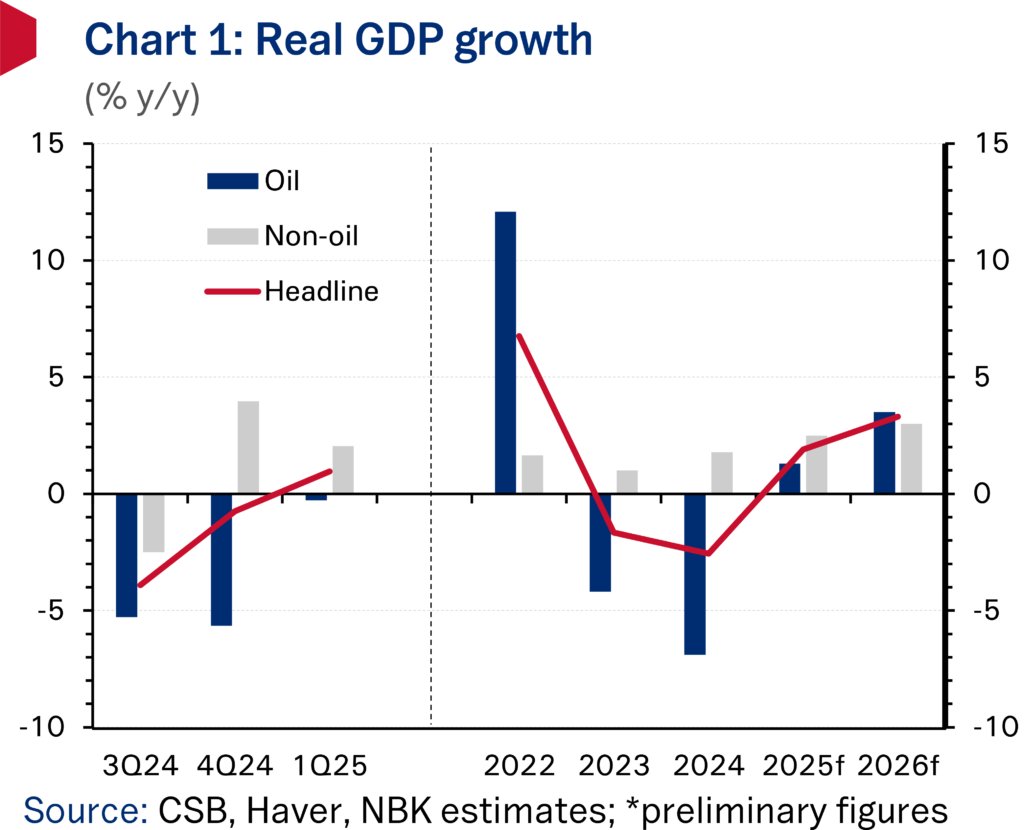
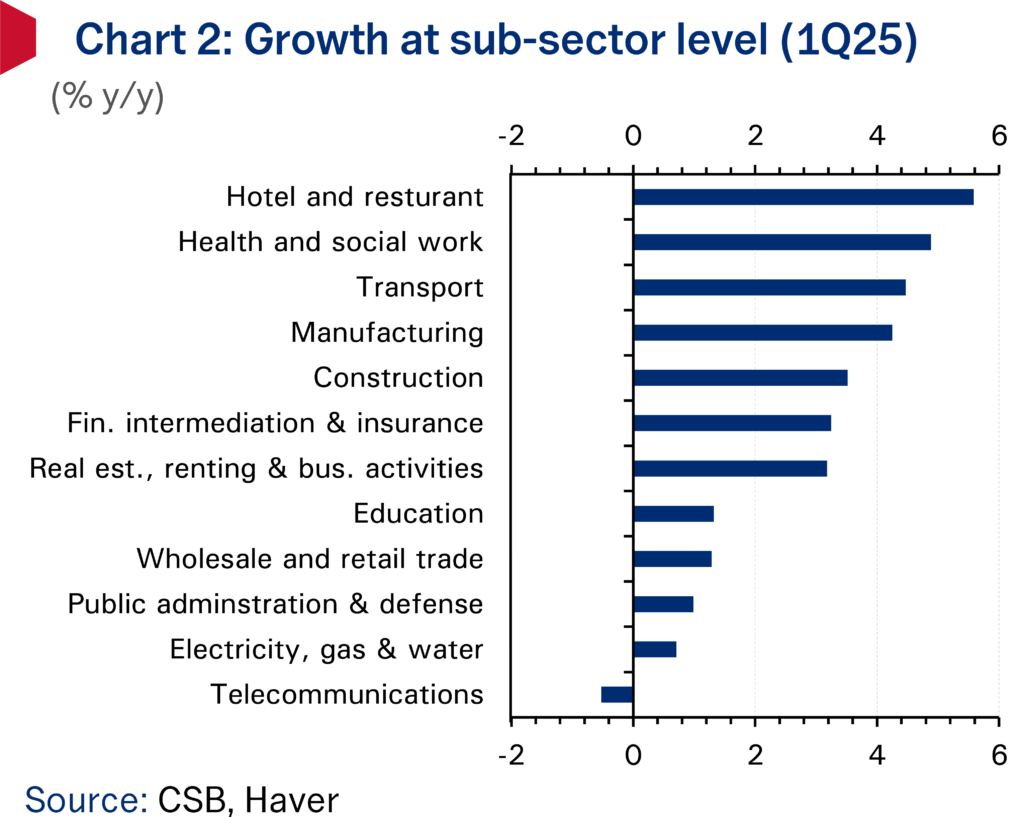
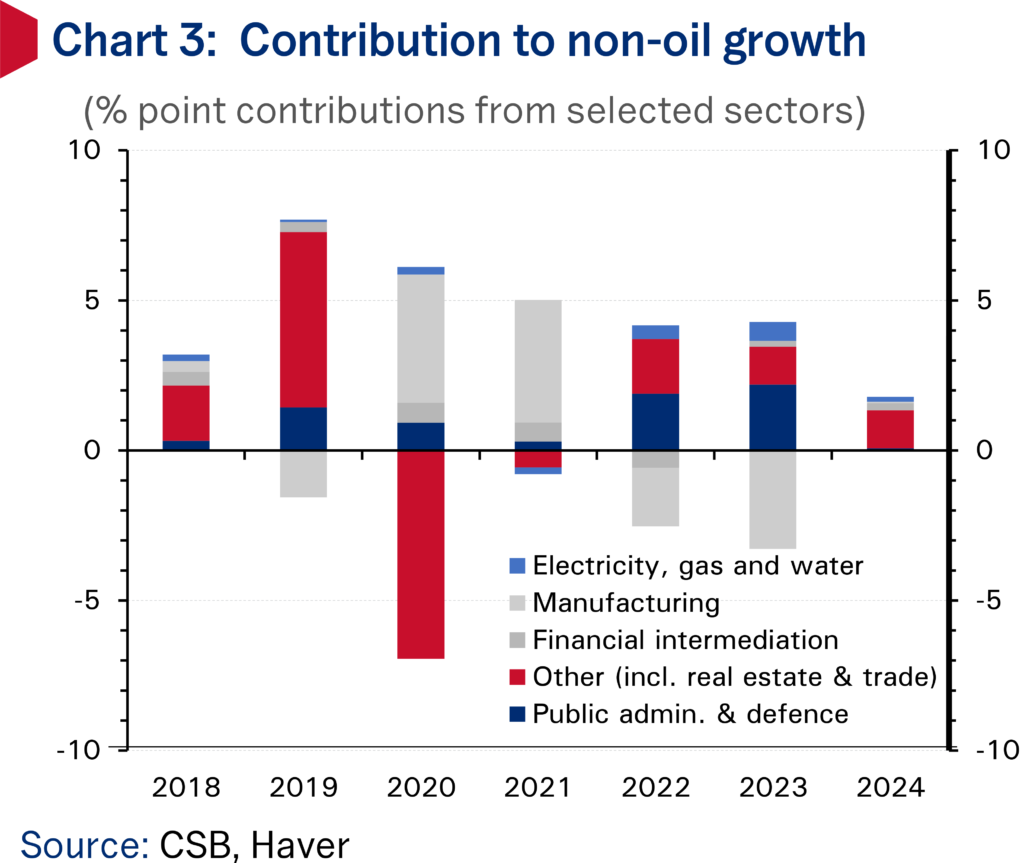
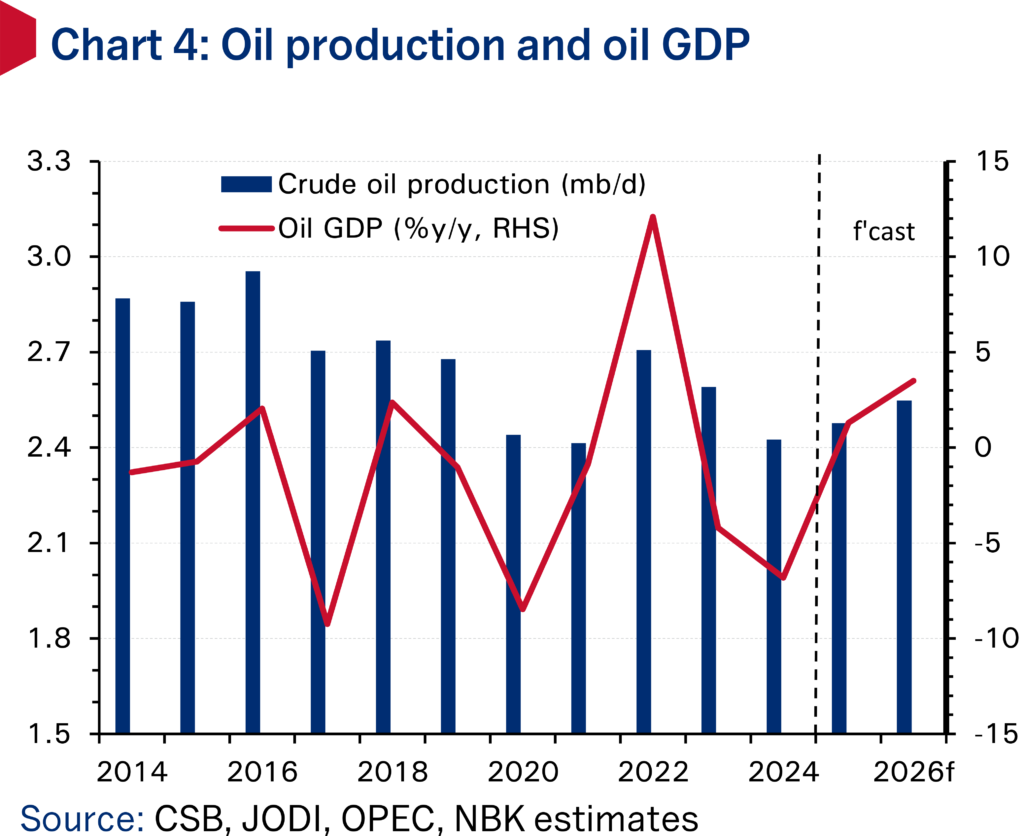
Dong Yu, now at Tsinghua, says via state media that Beijing-decreed, central govt bond-backed construction will continue into the next five years.
[from the Center for China & Globalization’s Pekingology]
by Zichen Wang, 10 August, 2025
The key concept in today’s newsletter is 国家重大战略实施和重点领域安全能力建设, in abbreviation in Chinese as 两重 liǎng zhòng.
In English, it is translated officially as the implementation of major national strategies and building up security capacity in key areas, hereinafter referred to as “Two Major Undertakings.”
The concept first appeared in official policy documents in the Chinese Premier’s Report on the Work of the Government [archived PDF] in March 2024.
To systematically address funding shortages facing some major projects for building a great country and advancing national rejuvenation, it is proposed that, starting this year and over each of the next several years, ultra-long special treasury bonds be issued. These bonds will be used to implement major national strategies and build up security capacity in key areas. One trillion yuan of such bonds will be issued in 2024.
By the end of the year, the yuan tag, despite being approved by the national legislature, had changed by 300 billion. The People’s Daily newspaper reported in December 2024.
As of now, the 700 billion yuan in ultra-long-term special treasury bonds allocated for the “two major undertakings” has been distributed in three batches to specific projects.
In 2025, the following year, the Report on the Work of the Government [archived PDF] says,
A total of 1.3 trillion yuan of ultra-long special treasury bonds will be issued, 300 billion yuan more than last year.
735 billion yuan will be earmarked in the central government budget for investment. We will put ultra-long special treasury bonds to good use, increase ultra-long-term loans and other types of financing support, and strengthen top-down organization and coordination to ensure greater support for the implementation of major national strategies and security capacity building in key areas.
A simultaneous Finance Ministry budget plan [archived PDF] rounds up the overall central government spending for the Two Major Undertakings to 800 billion yuan in 2025.
In yuan terms, the much-touted new government subsidies to households pale in comparison with the two major undertakings.
Also from the 2025 Report on the Work of the Government [archived PDF]:
Ultra-long special treasury bonds totaling 300 billion yuan will be issued to support consumer goods trade-in programs. This represents an increase of 150 billion yuan over the previous year.
This week, China announced this week that the phased free preschool education policy will cover all children in their final year of kindergartens, saving families 20 billion yuan. Childcare subsidies unveiled in July amount to 90 billion yuan.
As Joe Biden repeated over the years,
Don’t tell me what you value. Show me your budget, and I’ll tell you what you value.
The National Development and Reform Commission said last month:
In 2025, a total of 800 billion yuan has been allocated for the “two major undertakings,” supporting 1,459 projects in key areas such as ecological restoration in the Yangtze River Basin, major transportation infrastructure along the Yangtze River, the New Western Land–Sea Corridor, high-standard farmland, major water conservancy projects, urban underground pipeline networks, the “Three-North” shelterbelt program, and the renovation of hospital wards.
Now that the 2025 money has been spent by July and China is drawing up its next Five-Year Plan for 2026-2030, will there be more such projects in the future?
In a column for the state-run China News Service this week, Dong Yu, previously Deputy Director-General of the Second Economic Bureau of the Office of the Central Financial and Economic Affairs Commission and, before that, an official at China’s National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), pointedly said,
In the next step, during the formulation and implementation of the 15th Five-Year Plan, the “two major undertakings” will continue to occupy an important place, be organically incorporated into the new five-year plan, and form close alignment and sustained momentum with major national strategies, major plans, major projects, and key initiatives…
…Such a major strategy will be pursued with persistence—it will not remain rhetorical, nor will it be reversed abruptly.
He did not cite a source of information in his article.
Continuing with his lecturing style, Dong, now Executive Vice Director of China Institute for Development Planning, Tsinghua University, rebuked some unspecified market analysis that had observed the investments just were a one-time boost shot.
Some market institutions once analyzed that when China’s economy was facing short-term difficulties and challenges, the launch of the “two major undertakings” was mainly aimed at expanding investment in the short term to stabilize growth. Such a view clearly lacks a professional understanding of the decision-making intentions and logic, fails to properly grasp the relationship between the short term and the medium-to-long term, as well as between objectives and means, and inverts the proper order of priorities—a misconception that needs to be pointed out and corrected.
Dong also highlighted what he said was the unusual nature of the “strategic move,” including that central government debts fueled the investments, and they were selected “top-down,” rather than primarily relying on local government proposal or input.
The two undertakings were formally submitted for deliberation at the 2024 National People’s Congress after the central leadership made its decision and arrangements…
The central authorities have shown firm determination in this work, adopting the ultra-long-term special treasury bond—a macro policy tool that has rarely been used. Compared with several past issuances of special treasury bonds, the funding arrangement for the “two major undertakings” spans a longer cycle, has a broader scope of application, and will continue to advance in the next stage. It can be said that the scale and intensity are unprecedented. In 2024, a total of 700 billion yuan in ultra-long-term special treasury bonds was allocated, and in 2025, the figure is 800 billion yuan, all of which have now been fully disbursed.
The organization of the “two major undertakings” construction is top-down, completely different from the past practice in the investment sector where projects were determined through bottom-up applications. The purpose is to facilitate the smoother downward transmission of the needs of major national strategies. Relevant [central] government departments, by identifying shortcomings and weaknesses, specifying key areas, and refining project requirements, have ensured that the project list is no longer a collection of fragmented local items. Instead, projects are planned in an integrated manner by category and sector, with strengthened guidance for key regions, more targeted measures, and clearer standards.
Although an exhaustive list of the 1,459 projects does not appear to be available to the public, the “security capacity” build-up in the two major undertakings should be understood in broad terms, and Dong claims the investments put China on a sounder footing globally now that Donald Trump rules America again.
In recent years, the central authorities have emphasized security awareness and bottom-line thinking in development planning, a shift closely related to changes in the international situation. The closer China’s economy becomes intertwined with the global economy, the more comprehensive its considerations must be regarding issues such as food security, energy security, industrial security, and ecological security. The second “undertaking” in the “two major undertakings”—the strengthening of security capabilities in key areas—is precisely a forward-looking arrangement. The dramatic changes in the international environment since the beginning of 2025 have further underscored and confirmed the necessity of enhancing security capabilities, fully demonstrating that the central authorities’ thinking and deployment have been prescient and ahead of the curve.
Dong’s article via China News Service is fully translated below.
by Dong Yu, Executive Vice President, Institute for China Development Planning, Tsinghua University
The issuance of ultra-long-term special treasury bonds to support the implementation of major national strategies and the building of security capacities in key areas (hereinafter referred to as the “two major undertakings”) has become one of the hottest topics in China’s economy in recent years. Any observation of China’s present and future economic trajectory must include research and analysis of these two undertakings. More than a year has passed since the initiative was launched, making it both necessary and timely to evaluate its effectiveness, understand its operating mechanisms, and look ahead to its prospects.
The “Two Major Undertakings” Are by No Means Ordinary Policy Measures
In terms of decision-making background and process, as well as policy intensity and scope, the launch and implementation of the two major undertakings stand out from other policies. They represent a top-level design initiative.
Understanding a policy starts with its background. From the sequence of events leading to the proposal, this was a proactive, historic choice. The two undertakings were formally submitted for deliberation at the 2024 National People’s Congress after the central leadership made its decision and arrangements. The timing was significant: the 20th Communist Party of China National Congress had laid out a series of major long- and medium-term strategic initiatives that needed concrete engineering projects to push forward. China was midway through two Five-Year Plans, yet strategic advancement could not wait. The central leadership thus introduced the two major undertakings as a groundbreaking initiative.
Strategically, the undertakings directly address the needs of advancing long-term objectives. From the outset, they have been aimed squarely at the goals of Chinese modernization. By breaking down these goals into specific tasks and identifying the most difficult bottlenecks, the undertakings found their points of focus. Some of these tasks might take decades for other countries to achieve, but China has chosen not to delay—tackling them head-on at the starting stage of the new journey toward modernization. This model is uniquely Chinese and has been proven by history to be a key factor in China’s remarkable development successes.
The undertakings are also highly forward-looking—a “first move” by the central leadership. In recent years, national development planning has placed greater emphasis on security and on guarding the bottom line, in response to changes in the international environment. The closer China’s economy is linked to the global economy, the more comprehensive its considerations must be on food security, energy security, industrial security, and ecological security, and other issues. The second “major” in the initiative—security capacity building in key areas—is an arrangement made in anticipation of future challenges. The sharp changes in the international environment since 2025 have only highlighted and validated the necessity of strengthening security capacities, demonstrating that the central leadership’s thinking and arrangements were ahead of the curve.
The undertakings also have a strong overall and systemic quality, constituting a key move in macroeconomic governance. They focus on areas of outstanding importance to economic and social development and have a high degree of relevance to the overall development landscape. The policy toolkit they employ integrates investment, fiscal, science and technology, education, social, and ecological policies. This comprehensive package embodies the use of systems thinking to drive development and will significantly impact all aspects of the economy and society.
A Manifestation of Central Will
Extraordinary measures are for extraordinary tasks. The strategic objectives of Chinese modernization are long-term undertakings, and the two major undertakings provide the foundational support through systematic design and substantial funding.
The central leadership has committed to this initiative by adopting the rarely used macroeconomic tool of ultra-long-term special treasury bonds. Compared with previous special bond issuances, the funding for the two undertakings spans a longer cycle and serves a wider range of purposes, with plans for continued implementation. In both scale and intensity, this is unprecedented: 700 billion yuan in 2024 and 800 billion yuan in 2025, all of which has already been allocated.
In terms of priorities, it vividly reflects the principle of “concentrating resources to accomplish major undertakings.” The focus areas include urban–rural integration, regional coordination, high-quality population development, food security, energy and resource security, ecological security, and self-reliance and strength in science and technology—all crucial to building a strong nation and achieving national rejuvenation. These require coordinated planning and advancement. In just over a year, the high-level requirements have been translated into batches of concrete projects, reflecting the efficiency of implementation.
Project selection is guided by the principle that only the central government can resolve these issues. Some involve urgent development bottlenecks with significant obstacles that cannot be overcome by conventional means, such as scientific and technological breakthroughs, high-standard farmland construction, and upgrading the quality of higher education. Others are long-desired but previously unachievable projects that lack local willingness or capacity to implement, such as major cross-regional infrastructure, cross-basin wastewater treatment, and urban underground utility upgrades.
The organization of the “two major undertakings” construction is top-down, completely different from the past practice in the investment sector where projects were determined through bottom-up applications. The purpose is to facilitate the smoother downward transmission of the needs of major national strategies. Relevant [central] government departments, by identifying shortcomings and weaknesses, specifying key areas, and refining project requirements, have ensured that the project list is no longer a collection of fragmented local items. Instead, projects are planned in an integrated manner by category and sector, with strengthened guidance for key regions, more targeted measures, and clearer standards.
A Combination of “Hard” and “Soft” Measures
From the start, the undertakings were designed not only to fund “hard” engineering projects but also to include comprehensive arrangements for “soft” institutional and policy measures—an important innovation.
The emphasis on soft measures is pragmatic. Given the high importance and public nature of the projects, long-term mechanisms must be designed to ensure smooth progress during construction and sustainable operation thereafter. This includes drafting specialized plans to provide strategic guidance, introducing targeted policies to improve funding efficiency, and innovating institutional arrangements to safeguard implementation.
The implementation process is thus also a process of improving the investment and financing system, updating project management approaches, and enhancing investment effectiveness. In some sectors, soft-measure experiments have had positive impacts, creating healthy interaction with hard investments.
For example, the healthy operation of urban underground pipelines depends on sound maintenance mechanisms. Some local governments have attracted long-term institutional funds into major pipeline projects through debt or equity investment plans, stabilizing private sector returns via operational rights, government subsidies, and tax incentives. Others have introduced province-wide upstream–downstream gas price linkage, set reasonable water supply return rates based on market profits, and advanced the marketization of gas and water prices—reducing losses for public utilities and encouraging private investment.
Similarly, in the quality undergraduate expansion program, mechanisms play a guiding role: schools effectively implementing expansion plans receive increased support, while those performing poorly see reduced support; universities without expanded undergraduate admission plans are generally excluded from special bond funding. Disciplines and programs are adjusted dynamically to align talent training with economic and societal needs.
Directly Relevant to Everyone
The nature of the undertakings is not determined by project size but by their strategic objectives and significance. As long as they align with major national strategies, they are included—whether as large standalone projects, such as high-speed rail along the Yangtze River, or as “project packages,” such as Yangtze River wastewater treatment composed of multiple treatment facilities. This flexible, problem-oriented approach allows better alignment with public needs.
As projects break ground and enter operation, their benefits to people’s livelihoods will become increasingly evident. Observers should not see the undertakings as distant from daily life; they will bring tangible improvements to everyone’s quality of life.
For example:
- Urban underground pipelines: Upgrades to gas, water, and heating systems will greatly improve safety and resilience. Renovation of old gas pipelines is nearing completion, reducing accident rates by over 30%. Eliminating hidden risks in unseen places increases residents’ sense of security.
- Food security: Gradually converting all permanent basic farmland into high-standard farmland will stabilize grain output and enhance food safety. Higher standards mean safer products, so people will eat with greater confidence.
- Yangtze River protection: Building or upgrading over 60,000 kilometers of sewage pipelines in the Yangtze Economic Belt will greatly improve the river’s ecological environment and resolve long-standing public concerns.
- Transportation: Creating the shortest Shanghai–Chengdu high-speed rail corridor (approx. 1,900 km) will connect the Yangtze River Delta, the middle Yangtze region, and the Chengdu–Chongqing area more quickly, cutting travel time nearly in half and boosting east–west connectivity.
- Ecological security: Implementing the “Three-North” shelterbelt project over 130 million mu (93 million hectares), with good survival rates for trees, shrubs, and grasses, will safeguard northern ecological security and create new income opportunities.
- Higher education: “Double First-Class” universities will see markedly improved conditions, with over 500,000 new standard dorm beds. Quality undergraduate enrollment will rise by 16,000 in 2024 and over 20,000 in 2025, giving more students access to quality education and ensuring basic living needs for those from low-income families.
A Bold Stroke in the History of Development
The two major undertakings are a major decision by the CPC Central Committee and the State Council, aimed at the overall strategy of building a strong country and achieving national rejuvenation. They play an irreplaceable role in advancing Chinese modernization.
They are not short-term measures but focus on medium- to long-term development. Some market institutions once analyzed that when China’s economy was facing short-term difficulties and challenges, the launch of the “two major undertakings” was mainly aimed at expanding investment in the short term to stabilize growth. Such a view clearly lacks a professional understanding of the decision-making intentions and logic, fails to properly grasp the relationship between the short term and the medium-to-long term, as well as between objectives and means, and inverts the proper order of priorities — a misconception that needs to be pointed out and corrected.
Since implementation began, the undertakings have provided important support for economic stability. Although their starting point was not short-term growth, the resulting investment has boosted employment and consumption, helping to expand domestic demand and stabilize growth. In the next step, during the formulation and implementation of the 15th Five-Year Plan, the “two major undertakings” will continue to occupy an important place, be organically incorporated into the new five-year plan, and form close alignment and sustained momentum with major national strategies, major plans, major projects, and key initiatives.
They will also bolster the country’s core competitiveness. As foundational support for Chinese modernization, they will strengthen factor security and resolve long-term bottlenecks, with far-reaching significance for shaping China’s development prospects. In an era of intensifying major-power competition, they will provide stable expectations and significantly enhance China’s capacity to manage international uncertainty. Such a major strategy will be pursued with persistence—it will not remain rhetorical, nor will it be reversed abruptly.
Though implementation has only recently begun, the undertakings’ historic role will continue to grow over time. In the future, looking back, they will surely stand as an important part of the “China story” and leave a bold stroke in the history of the People’s Republic’s development.