[from NBK Group’s Economic Research Department, 21 November, 2024]
Kuwait: Solid credit growth in October driven by household credit. Domestic credit increased by a solid 0.4% in October, driving up YTD growth to 2.9% (3.2% y/y). The recovery in household credit continued, with growth in October at a solid 0.5%, resulting in a YTD increase of 2.4%. While y/y growth in household credit remains a limited 2.3%, annualized growth over the past four months is a stronger 4.7%. Business credit inched up by 0.2% in October, pushing YTD growth to 3.6% (2.9% y/y). Industry and trade drove business credit growth in October while construction and trade are the fastest growing YTD at 17% and 8%, respectively. In contrast, the oil/gas sector continued its downtrend, deepening the YTD decrease to 13%. Excluding the oil/gas sector, growth in business credit would increase to a relatively good 5% YTD. Looking ahead, the last couple of months of the year (especially December) are usually the weakest for business credit, likely due to increased repayments and write-offs, but it will not be surprising if the recovery in household credit is generally sustained, especially given the commencement of the interest rate-cutting cycle. Meanwhile, driven by a plunge in the volatile public-institution deposits, resident deposits decreased in October, resulting in YTD growth of 2.4% (4.2% y/y). Private-sector deposits inched up in October driving up YTD growth to 4.5% compared with 10% for government deposits while public-institution deposits are a big drag (-14%). Within private-sector KD deposits, CASA showed further signs of stabilization as there was no decrease for the third straight month while the YTD drawdown is a limited 1%.
Chart 1: Kuwait credit growth
(% y/y)
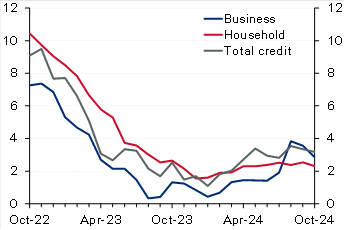
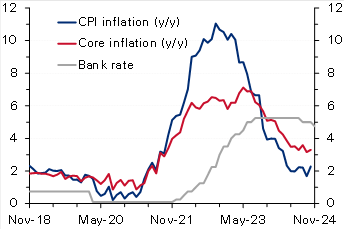
Chart 2: UK inflation
(%)
Egypt: IMF concludes mission for fourth review, sees external risks. The IMF concluded its visit to Egypt after spending close to 2 weeks, holding several in-person meetings with the Egyptian authorities, private sector, and other stakeholders. The IMF released a statement mentioning that the current ongoing geopolitical tensions in the region in addition to an increasing number of refugees have affected the external sector (Suez Canal receipts down by 70%) and put severe pressure on the fiscal front. The Fund acknowledged the Central Bank of Egypt’s commitment to unify the exchange rate, maintain the flexible exchange rate regime, and keep inflation on a firm downward trend over the medium term by substantially tightening monetary policy. It also highlighted that continued policy discipline was also a key to containing fiscal risks, especially those related to the energy sector. The Fund, as always, re-iterated the need for promoting the private sector mainly through an enhanced tax system and accelerating divestment plans of the state firms. Finally, it also said that the discussions would continue over the coming days to finalize the agreement on the remaining policies and reform plans. However, the release did not provide any clear hints about the conclusion on the government’s earlier request to push the timeline of some of the subsidy moves.
Oman: IMF completes article IV with a strong outlook for the economy in 2025. Oman’s economy continued to expand with growth reaching 1.9% in the first half of 2024 (versus 1.2% in 2023), despite being weighed down by OPEC+ mandated oil production cuts as non-oil GDP grew a stronger 3.8% y/y in H1 (versus 1.8% in 2023). The fiscal and current account balances remain in a comfortable situation evident by a decline in public sector debt and the recent rating upgrade to investment grade. The Fund expects Oman’s economic growth to see a strong rebound in 2025, supported by higher oil production. It also believes that fiscal and current account balances will remain in surplus but at lower levels. Key risks to the outlook stem from oil price volatility and intensifying geopolitical tensions. The IMF also mentioned that further efforts are needed to raise nonhydrocarbon revenues through more tax policy measures and the phasing out of untargeted subsidies which should help in freeing up resources to finance growth under the government’s diversification agenda.
UK: Inflation rises more than forecast, reinforcing BoE’s caution on rate cuts. UK CPI inflation increased to 2.3% y/y in October from 1.7% the previous month, slightly above the market and the Bank of England’s forecast of 2.2%. On a monthly basis too, inflation rose to 0.6%, a seven-month high, from September’s no change. The steep rise was mainly driven by an almost 10% rise in the household energy price cap effective from October. Core inflation also accelerated to 3.3% y/y (0.4% m/m) from 3.2% (0.1% m/m). While goods prices continued to fall (-0.3% y/y), service prices rose at a faster rate of 5% from 4.9%. Recently, the Bank of England had cautioned about inflation quickening next year (projecting a peak rate of 2.8% in Q3 2025), citing the impact of higher insurance contributions and rising minimum wages as outlined in the latest government budget. Therefore, with inflation rising above forecast, the bank will likely slow the pace of monetary easing after delivering two interest rate cuts of 25 bps earlier, with markets now seeing only two additional cuts by the end of 2025.
Eurozone: ECB warns of fiscal and growth risks in its latest Financial Stability Review [archived PDF]. In its most recent Financial Stability Review (November) [archived PDF], the European Central Bank warned that elevated debt and fiscal deficit levels and anemic long-term growth could expose sovereign debt vulnerabilities in the region, stoking concerns of a repeat of the 2011 sovereign debt crisis. Maturing debt being rolled over at much higher borrowing rates raising debt service costs poses risks to countries with little fiscal space and leaves certain governments exposed to market fluctuations. The bank also emphasized the risks of high equity valuations, low liquidity and a greater concentration of exposure among non-banks. Moreover, it sees current geopolitical uncertainties and the possibility of more trade tensions as heightening risks. The Eurozone’s current government debt-to-GDP ratio stands at 88%, but the underlying data suggest a much more precarious situation with Greece, Italy, and France’s ratios at 164%, 137% and 112%. Recently, concerns about France’s high fiscal deficit (around 5.9% of GDP) and elevated debt levels saw yields on the country’s bonds rise steeply, widening the spread gap with German bonds to the highest level in over a decade.
| Stock markets | Index | Daily Change (%) | YTD Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regional | |||
| Abu Dhabi (ADI) | 9,405 | -0.23 | -1.80 |
| Bahrain (ASI) | 2,043 | -0.37 | 3.62 |
| Dubai (DFMGI) | 4,761 | 0.61 | 17.26 |
| Egypt (EGX 30) | 30,588 | -0.33 | 23.18 |
| GCC (S&P GCC 40) | 709 | 0.09 | -0.52 |
| Kuwait (All Share) | 7,353 | -0.08 | 7.86 |
| KSA (TASI) | 11,868 | -0.07 | -0.83 |
| Oman (MSM 30) | 4,609 | 0.00 | 2.10 |
| Qatar (QE Index) | 10,438 | 0.12 | -3.62 |
| International | |||
| CSI 300 | 3,986 | 0.22 | 16.17 |
| DAX | 19,005 | -0.29 | 13.45 |
| DJIA | 43,408 | 0.32 | 15.17 |
| Eurostoxx 50 | 4,730 | -0.45 | 4.60 |
| FTSE 100 | 8,085 | -0.17 | 4.55 |
| Nikkei 225 | 38,352 | -0.16 | 14.61 |
| S&P 500 | 5,917 | 0.00 | 24.05 |
| 3m interbank rates | % | Daily Change (bps) | YTD Change (bps) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bahrain | 5.86 | -1.29 | -66.34 |
| Kuwait | 3.94 | 0.00 | -37.50 |
| Qatar | 6.00 | 0.00 | -25.00 |
| UAE | 4.43 | 3.81 | -89.96 |
| Saudi | 5.50 | -4.75 | -73.14 |
| SOFR | 4.52 | -0.09 | -81.13 |
| Bond yields | % | Daily Change (bps) | YTD Change (bps) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regional | |||
| Abu Dhabi 2027 | 4.66 | 5.00 | 33.9 |
| Oman 2027 | 5.49 | 6.00 | 33.0 |
| Qatar 2026 | 4.68 | 6.00 | 16.1 |
| Kuwait 2027 | 4.69 | 3.00 | 35.0 |
| Saudi 2028 | 4.96 | 1.00 | 43.9 |
| International 10-year | |||
| US Treasury | 4.41 | 1.77 | 55.3 |
| German Bund | 2.34 | 0.35 | 31.2 |
| UK Gilt | 4.47 | 2.60 | 93.0 |
| Japanese Gov’t Bond | 1.07 | 1.0 | 45.4 |
| Exchange rates | Rate | Daily Change (%) | YTD Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| KWD per USD | 0.31 | 0.04 | -0.05 |
| KWD per EUR | 0.32 | -0.46 | -1.98 |
| USD per EUR | 1.05 | -0.49 | -4.47 |
| JPY per USD | 155.43 | 0.50 | 10.19 |
| USD per GBP | 1.27 | -0.25 | -0.62 |
| EGP per USD | 49.67 | 0.34 | 61.00 |
| Commodities | $/unit | Daily Change (%) | YTD Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brent crude | 72.81 | -0.68 | -5.49 |
| KEC | 73.78 | 0.74 | -7.26 |
| WTI | 68.87 | -0.75 | -3.88 |
| Gold | 2,648.2 | 0.80 | 28.40 |
Disclaimer: While every care has been taken in preparing this publication, National Bank of Kuwait accepts no liability whatsoever for any direct or consequential losses arising from its use. Daily Economic Update is distributed on a complimentary and discretionary basis to NBK clients and associates. This report and previous issues can be found in the “News & Insight / Economic Reports” section of the National Bank of Kuwait’s web site. Please visit their web site, nbk.com, for other bank publications.